JSON export format
This page describes Spine's JSON export format for skeleton and animation data. The Spine Runtimes load this data to display animations. Also, Spine can import data in this format, allowing interoperability with other tools. JSON export files can be found for each example project in the Spine Runtimes.
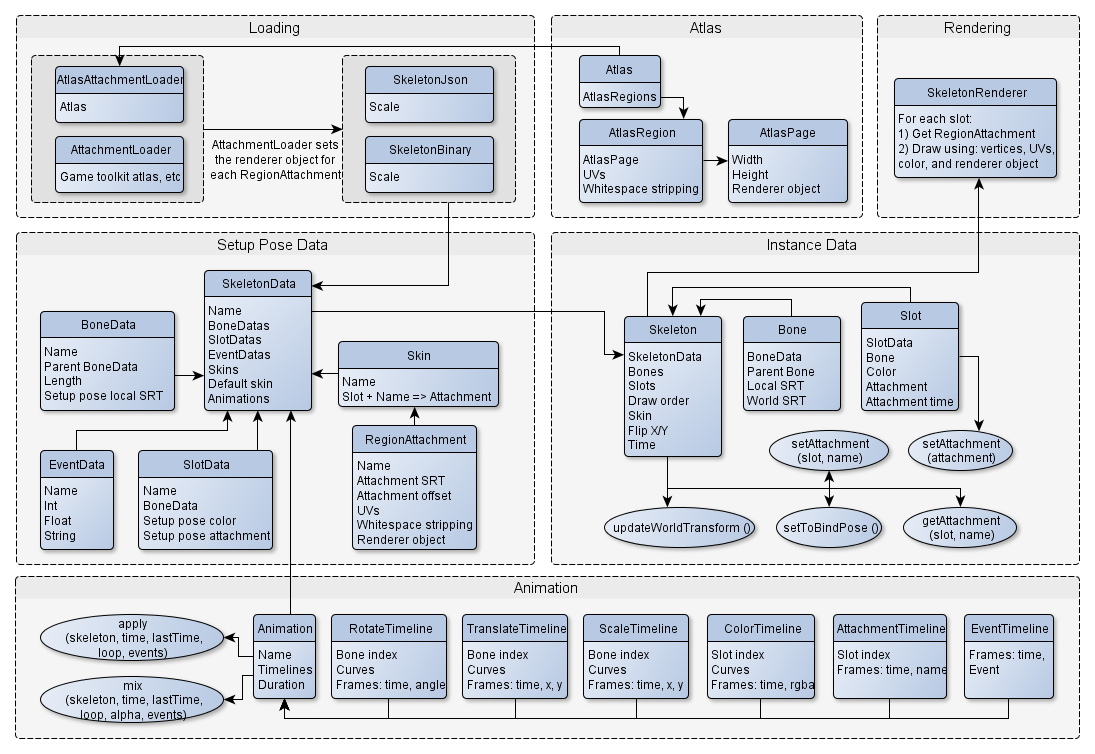
The Spine Runtimes handle loading JSON and binary data. You do not need to write your own loading code unless you are writing your own runtime from scratch (which is an enormous amount of work).
The JSON format is human readable and editable, especially when used with the "pretty print" setting. This makes it a good choice when needing to manually inspect or otherwise process the data. It is also resistant to minor changes in the runtimes, which may prevent the need to re-export the data when the runtime changes. The downside is that the JSON format has a larger file size than the binary format and is slower to load at runtime.
Data marked "nonessential" is only output when the Nonessential data export setting is checked. This data is not required for rendering but may be useful for tools or when importing the data back into Spine.
The JSON format is the serialized version of a "skeleton data" instance, which has a list of bones, slots, skins, and animations. This is stateless data that is not tied to a particular on-screen skeleton instance.
Skeleton
The skeleton section stores metadata about the skeleton.
Example skeleton JSON:
"hash": "5WtEfO08B0TzTg2mDqj4IHYpUZ4",
"spine": "3.8.24",
"x": -17.2,
"y": -13.3,
"width": 470.86,
"height": 731.44,
"images": "./images/",
"audio": "./audio/"
},
Skeleton attributes:
- hash: A hash of all the skeleton data. This can be used by tools to detect if the data has changed since the last time it was loaded.
- version: The version of Spine that exported the data. This can be used by tools to enforce a particular Spine version to be used.
- x: The x-coordinate of the bottom left corner of the AABB for the skeleton's attachments as it was in the setup pose in Spine.
- y: The y-coordinate of the bottom left corner of the AABB for the skeleton's attachments as it was in the setup pose in Spine.
- width: The AABB width for the skeleton's attachments as it was in the setup pose in Spine. This can be used as a general size of the skeleton, though the skeleton's AABB depends on how it is posed.
- height: The AABB height for the skeleton's attachments as it was in the setup pose in Spine.
- fps: The dopesheet framerate in frames per second, as it was in Spine. Assume 30 if omitted. Nonessential.
- images: The images path, as it was in Spine. Nonessential.
- audio: The audio path, as it was in Spine. Nonessential.
Bones
The bones section describes the bones in the setup pose.
Example bones skeleton JSON:
{ "name": "root" },
{ "name": "torso", "parent": "root", "length": 85.82, "x": -6.42, "y": 1.97, "rotation": 94.95 },
...
],
Bones are ordered so that the parent always comes before a child bone.
Bone attributes:
- name: The bone name. This is unique for the skeleton.
- length: The length of the bone. The bone length is not typically used at runtime except to draw debug lines for the bones. Assume 0 if omitted.
- transform: Determines how parent bone transforms are inherited: normal, onlyTranslation, noRotationOrReflection, noScale, or noScaleOrReflection. Assume normal if omitted.
- skin: If true, the bone is only active when the active skin has the bone. Assume false if omitted.
- x: The X position of the bone relative to the parent for the setup pose. Assume 0 if omitted.
- y: The Y position of the bone relative to the parent for the setup pose. Assume 0 if omitted.
- rotation: The rotation in degrees of the bone relative to the parent for the setup pose. Assume 0 if omitted.
- scaleX: The X scale of the bone for the setup pose. Assume 1 if omitted.
- scaleY: The Y scale of the bone for the setup pose. Assume 1 if omitted.
- shearX: The X shear of the bone for the setup pose. Assume 0 if omitted.
- shearY: The Y shear of the bone for the setup pose. Assume 0 if omitted.
- color: The color of the bone, as it was in Spine. Assume 0x989898FF RGBA if omitted. Nonessential.
Slots
The slots section describes the draw order and the available slots where attachments can be assigned.
Example slots skeleton JSON:
{ "name": "left shoulder", "bone": "left shoulder", "attachment": "left-shoulder" },
{ "name": "left arm", "bone": "left arm", "attachment": "left-arm" },
...
],
The "slots" section may be omitted if there are no slots. Slots are ordered in the setup pose draw order. Images in higher index slots are drawn on top of those in lower index slots.
Slot attributes:
- name: The slot name. This is unique for the skeleton.
- bone: The name of the bone that this slot is attached to.
- color: The color of the slot for the setup pose. This is an 8 character string containing 4 two digit hex numbers in RGBA order. Assume "FF" for alpha if alpha is omitted. Assume "FFFFFFFF" if omitted.
- dark: The dark color of the slot for the setup pose, used for two color tinting. This is a 6 character string containing 3 two digit hex numbers in RGB order. Omitted when two color tinting is not used.
- attachment: The name of the slot's attachment for the setup pose. Assume no attachment for the setup pose if omitted.
- blend: The type of blending to use when drawing the slot's visible attachment: normal, additive, multiply, or screen.
Constraints
IK constraints
This section describes the IK constraints.
{
"name": "left leg",
"order": 2,
"bones": [ "left thigh", "left shin" ],
"target": "left ankle",
"mix": 0.5,
"bendPositive": false,
"compress": true,
},
...
],
The "ik" section may be omitted if there are no IK constraints.
IK constraint attributes:
- name: The constraint name. This is unique for the skeleton.
- order: The ordinal for the order constraints are applied.
- skin: If true, the constraint is only applied when the active skin has the constraint. Assume false if omitted.
- bones: A list of 1 or 2 bone names whose rotation will be controlled by the constraint.
- target: The name of the target bone.
- mix: A value from 0 to 1 indicating the influence the constraint has on the bones, where 0 means only FK, 1 means only IK, and between is a mix of FK and IK. Assume 1 if omitted.
- softness: A value for two bone IK, the distance from the maximum reach of the bones that rotation will slow. Assume 0 if omitted.
- bendPositive: If true, the bones will bend in the positive rotation direction. Assume true if omitted.
- compress: If true, and only a single bone is being constrained, if the target is too close, the bone is scaled to reach it. Assume false if omitted.
- stretch: If true, and if the target is out of range, the parent bone is scaled to reach it. If more than one bone is being constrained and the parent bone has local nonuniform scale, stretch is not applied. Assume false if omitted.
- uniform: If true, and only a single bone is being constrained, and compress or stretch is used, the bone is scaled on both the X and Y axes. Assume false if omitted.
Transform constraints
This section describes the transform constraints.
{ "name": "weapon to hip", "order": 1, "bone": "weapon", "target": "hip" },
...
],
The "transform" section may be omitted if there are no transform constraints.
Transform constraint attributes:
- name: The constraint name. This is unique for the skeleton.
- order: The ordinal for the order constraints are applied.
- skin: If true, the constraint is only applied when the active skin has the constraint. Assume false if omitted.
- bones: The bones whose transform will be controlled by the constraint.
- target: The name of the target bone.
- rotation: The rotation to offset from the target bone. Assume 0 if omitted.
- x: The X distance to offset from the target bone. Assume 0 if omitted.
- y: The Y distance to offset from the target bone. Assume 0 if omitted.
- scaleX: The X scale to offset from the target bone. Assume 0 if omitted.
- scaleY: The Y scale to offset from the target bone. Assume 0 if omitted.
- shearY: The Y shear to offset from the target bone. Assume 0 if omitted.
- rotateMix: A value from 0 to 1 indicating the influence the constraint has on the bones, where 0 means no affect, 1 means only the constraint, and between is a mix of the normal pose and the constraint. Assume 1 if omitted.
- translateMix: See rotateMix.
- scaleMix: See rotateMix.
- shearMix: See rotateMix.
- local: True if the target's local transform is affected, else the world transform is affected. Assume false if omitted.
- relative: True if the target's transform is adjusted relatively, else the transform is set absolutely. Assume false if omitted.
Path constraints
This section describes the path constraints.
{
"name": "constraintName",
"order": 0,
"bones": [ "boneName1", "boneName2" ],
"target": "slotName",
"positionMode": "fixed",
"spacingMode": "length",
"rotateMode": "tangent",
"rotation": "45",
"position": "204",
"spacing": "10",
"rotateMix": "0",
"translateMix": "1"
},
...
],
The "path" section may be omitted if there are no path constraints.
Path constraint attributes:
- name: The constraint name. This is unique for the skeleton.
- order: The ordinal for the order constraints are applied.
- skin: If true, the constraint is only applied when the active skin has the constraint. Assume false if omitted.
- bones: The bones whose rotation and/or translation will be controlled by the constraint.
- target: The name of the target slot.
- positionMode: Determines how the path position is calculated: fixed or percent. Assume percent if omitted.
- spacingMode: Determines how the spacing between bones is calculated: length, fixed, or percent. Assume length if omitted.
- rotateMode: Determines how the bone rotation is calculated: tangent, chain, or chain scale. Assume tangent if omitted.
- rotation: The rotation to offset from the path rotation. Assume 0 if omitted.
- position: The path position. Assume 0 if omitted.
- spacing: The spacing between bones. Assume 0 if omitted.
- rotateMix: A value from 0 to 1 indicating the influence the constraint has on the bones, where 0 means no affect, 1 means only the constraint, and between is a mix of the normal pose and the constraint. Assume 1 if omitted.
- translateMix: See rotateMix.
Skins
Each skin described in the skins section describes attachments that can be assigned to each slot.
Example skins skeleton JSON:
{
"name": "skinName",
"attachments": {
"slotName": {
"attachmentName": { "x": -4.83, "y": 10.62, "width": 63, "height": 47 },
...
},
...
}
},
{
"name": "skinName",
"attachments": {
"slotName": {
"attachmentName": { "name": "actualAttachmentName", "x": 53.94, "y": -5.75, "rotation": -86.9, "width": 121, "height": 132 },
...
},
...
}
},
...
],
The "skins" section may be omitted if there are no skins or attachments.
Each skin is essentially a map with a compound key consisting of a slot and attachment name and the value is an attachment. The attachment name used in the key is the same for each skin, but the actual attachment name for the attachment may vary.
For example, the "pelvis" image for the "pelvis" slot might have an actual attachment name of "red/pelvis" for the "red" skin and "blue/pelvis" for the "blue" skin. If a skeleton has the "blue" skin active and is told to show the "pelvis" image for the "pelvis" slot, the attachment it finds would have an actual attachment name of "blue/pelvis".
When a skeleton needs to find an attachment for a slot, it first checks its skin. If not found, the skeleton then checks its default skin. The default skin contains attachments that are not defined by a skin in Spine, allowing mixed usage of skin and non-skin attachments. The default skin always has the name "default".
Skins other than the default skin may have bones and/or constraints:
{
"name": "skinName",
"bones": [ "bone1", "bone2" ],
"ik": [ "ik1", "ik2" ],
"transform": [ "transform1", "transform2" ],
"path": [ "path1", "path2" ],
"attachments": {
...
}
},
...
}
Attachments
The attributes for each attachment vary based on the attachment type.
Common attachment attributes:
- type: The type of attachment. Assume "region" if omitted.
- name: The attachment name. This is unique for the skeleton. For image attachments this is a key used to look up the texture region, for example on disk or in a texture atlas. If omitted, the key from the surrounding JSON map is used as the actual attachment name.
Attachment type:
- region: A textured rectangle.
- mesh: A textured mesh whose vertices may be influenced by multiple bones using weights.
- linkedmesh: A mesh which shares the UVs, vertices, and weights of another mesh.
- boundingbox: A polygon used for hit detection, physics, etc.
- path: A cubic spline, often used for moving bones along a path.
- point: A single point and a rotation, often used for spawning projectiles or particles.
- clipping: A polygon used to clip drawing of other attachments.
region attachment attributes:
- path: If set, this value is used instead of the attachment name to look up the texture region.
- x: The X position of the image relative to the slot's bone. Assume 0 if omitted.
- y: The Y position of the image relative to the slot's bone. Assume 0 if omitted.
- scaleX: The X scale of the image. Assume 1 if omitted.
- scaleY: The Y scale of the image. Assume 1 if omitted.
- rotation: The rotation in degrees of the image relative to the slot's bone. Assume 0 if omitted.
- width: The width of the image.
- height: The height of the image.
- color: The color to tint the attachment. Assume FFFFFFFF RGBA if omitted.
mesh attachment attributes:
- path: If set, this value is used instead of the attachment name to look up the texture region.
- uvs: A list of number pairs that are the texture coordinates for each vertex.
- triangles: A list of vertex indices that define each triangle for the mesh.
- vertices: For each vertex either an x,y pair or, for a weighted mesh, first the number of bones which influence the vertex, then for that many bones: bone index, bind position X, bind position Y, weight. A mesh is weighted if the number of vertices > number of UVs.
- hull: The number of vertices that make up the polygon hull. The hull vertices are always first in the vertices list.
- edges: A list of vertex index pairs that define the edges between connected vertices. Nonessential.
- color: The color to tint the attachment. Assume FFFFFFFF RGBA if omitted.
- width: The width of the image used by the mesh. Nonessential.
- height: The height of the image used by the mesh. Nonessential.
linkedmesh attachment attributes:
- path: If set, this value is used instead of the attachment name to look up the texture region.
- skin: The skin that contains the source mesh. If omitted, the source mesh is in the default skin.
- parent: The name of the source mesh, which is always in the same slot as this mesh. If the source mesh is not in the default skin, this name is used to look up the actual attachment in the skin.
- deform: If false, deform timelines for the source mesh are not applied to this mesh. Assume true if omitted.
- color: The color to tint the attachment. Assume FFFFFFFF RGBA if omitted.
- width: The width of the image used by the mesh. Nonessential.
- height: The height of the image used by the mesh. Nonessential.
boundingbox attachment attributes:
- vertexCount: The number of bounding box vertices.
- vertices: For each vertex either an x,y pair or, for a weighted bounding box, first the number of bones which influence the vertex, then for that many bones: bone index, bind position X, bind position Y, weight. A bounding box is weighted if the number of vertices > vertex count.
- color: The color of the bounding box in Spine. Assume 60F000FF RGBA if omitted. Nonessential.
path attachment attributes:
- closed: True if the last and first vertex are connected. Assume false if omitted.
- constantSpeed: True if movement along the path uses constant speed. Assume true if omitted.
- lengths: The length in the setup pose from the start of the path to the end of each curve.
- vertexCount: The number of path vertices.
- vertices: For each vertex either an x,y pair or, for a weighted path, first the number of bones which influence the vertex, then for that many bones: bone index, bind position X, bind position Y, weight. A path is weighted if the number of vertices > vertex count.
- color: The color of the path in Spine. Assume FF7F00FF RGBA if omitted. Nonessential.
point attachment attributes:
- x: The X position of the point relative to the slot's bone. Assume 0 if omitted.
- y: The Y position of the point relative to the slot's bone. Assume 0 if omitted.
- rotation: The rotation in degrees of the point relative to the slot's bone. Assume 0 if omitted.
- color: The color of the point in Spine. Assume F1F100FF RGBA if omitted. Nonessential.
clipping attachment attributes:
- end: The name of the slot where clipping stops.
- vertexCount: The number of clipping polygon vertices.
- vertices: For each vertex either an x,y pair or, for a weighted clipping polygon, first the number of bones which influence the vertex, then for that many bones: bone index, bind position X, bind position Y, weight. A clipping polygon is weighted if the number of vertices > vertex count.
- color: The color of the clipping attachment in Spine. Assume CE3A3AFF RGBA if omitted. Nonessential.
Events
The events sections describes the named events that can be triggered during animations and their setup pose values.
Example events JSON:
"name": { "int": 1, "float": 2, "string": "three" },
"name": { "int": 1, "float": 2, "string": "three", "audio": "hit.wav", "volume": 0.9, "balance": -0.25 },
...
],
Event attributes:
- name: The name of the event. This is unique for the skeleton.
- int: The integer value of the event. Assume 0 if omitted.
- float: The float value of the event. Assume 0 if omitted.
- string: The string value of the event. Assume null if omitted.
- audio: The path to an audio file if this event is intended to play audio. Assume null if omitted.
- volume: The volume used to play the audio file. Assume 1 if omitted.
- balance: The stereo balance used to play the audio file. Assume 0 if omitted.
Animations
An animation has a list of timelines. Each timeline has a list keyframes that describe how values for a bone or slot change over time.
Example bones animation JSON:
"name": {
"bones": { ... },
"slots": { ... },
"ik": { ... },
"deform": { ... },
"events": { ... },
"draworder": { ... },
},
...
}
Bone timelines
The bones section of an animation describes timelines that manipulate bones.
Example bones animation JSON:
"bones": {
"boneName": {
"timelineType": [
{ "time": 0, "angle": -26.55 },
{ "time": 0.1333, "angle": -8.78 },
...
],
...
},
...
},
The attributes for each keyframe vary based on the timeline type.
Bone timeline types:
- rotate: Keyframes for a bone's rotation.
- translate: Keyframes for a bone's X and Y position.
- scale: Keyframes for a bone's X and Y scale.
- shear: Keyframes for a bone's X and Y shear.
Common bone keyframe attributes:
- time: The time in seconds for the keyframe. Assume 0 if omitted.
- curve: The interpolation to use between this and the next keyframe. If the attribute is omitted the curve is linear, if the value is the string "stepped" the curve is stepped, otherwise the value is an array with 4 elements which define the control points:
cx1,cy1,cx2, andcy2. The X axis unit is frame and the Y axis unit is value.
rotate keyframe attributes:
- angle: The bone's rotation relative to the setup pose. Assume 0 if omitted.
translate keyframe attributes:
- x: The bone's X position relative to the setup pose. Assume 0 if omitted.
- y: The bone's Y position relative to the setup pose. Assume 0 if omitted.
scale keyframe attributes:
- x: The bone's X scale relative to the setup pose. Assume 1 if omitted.
- y: The bone's Y scale relative to the setup pose. Assume 1 if omitted.
shear keyframe attributes:
- x: The bone's X shear relative to the setup pose. Assume 0 if omitted.
- y: The bone's Y shear relative to the setup pose. Assume 0 if omitted.
Slot timelines
The slots section of an animation describes timelines that manipulate slots.
Example slots animation JSON:
"slotName": {
"timelineType": [
{ "time": 0.2333, "name": "eyes closed" },
{ "time": 0.6333, "name": "eyes open" },
...
],
...
},
...
}
The attributes for each keyframe vary based on the timeline type.
Slot timeline types:
- attachment: Keyframes for changing a slot's attachment.
- color: Keyframes for changing a slot's color.
Common slot keyframe attributes:
- time: The time in seconds for the keyframe.
attachment keyframe attributes:
- name: The name of the attachment to set for the slot.
color keyframe attributes:
- color: The color to set for the slot. This is an 8 character string containing 4 two digit hex numbers in RGBA order.
- curve: The interpolation to use between this and the next keyframe. If the attribute is omitted the curve is linear, if the value is the string "stepped" the curve is stepped, otherwise the value is
cx1for a Bézier curve.
A Bézier curve has 4 elements which define the control points:cx1,cy1,cx2,cy2. The X axis is from 0 to 1 and represents the percent of time between the two keyframes. The Y axis is from 0 to 1 and represents the percent of the difference between the keyframe's values. - c2: The
cy1value for a Bézier curve. Assume 0 if omitted. - c3: The
cx2value for a Bézier curve. Assume 1 if omitted. - c4: The
cy2value for a Bézier curve. Assume 1 if omitted.
twoColor keyframe attributes:
- light: The light color to set for the slot. This is an 8 character string containing 4 two digit hex numbers in RGBA order.
- dark: The dark color to set for the slot. This is an 8 character string containing 4 two digit hex numbers in RGBA order.
- curve: The interpolation to use between this and the next keyframe. If the attribute is omitted the curve is linear, if the value is a string the curve is stepped, otherwise the value is
cx1for a Bézier curve.
A Bézier curve has 4 elements which define the control points:cx1,cy1,cx2,cy2. The X axis is from 0 to 1 and represents the percent of time between the two keyframes. The Y axis is from 0 to 1 and represents the percent of the difference between the keyframe's values. - c2: The
cy1value for a Bézier curve. - c3: The
cx2value for a Bézier curve. - c4: The
cy2value for a Bézier curve.
IK constraint timeline
The IK section of an animation describes timelines for IK constraints.
Example IK animation JSON:
"constraintName": [
{ "time": 0.5333, "mix": 0.616, "bendPositive": true },
...
],
...
},
IK constraint keyframe attributes:
- time: The time in seconds for the keyframe.
- mix: The IK constraint mix for the keyframe. Assume 1 if omitted.
- softness: A value for two bone IK, the distance from the maximum reach of the bones that rotation will slow. Assume 0 if omitted.
- bendPositive: The IK constraint bend direction for the keyframe. Assume false if omitted.
- compress: If true, and only a single bone is being constrained, if the target is too close, the bone is scaled to reach it. Assume false if omitted.
- stretch: If true, and if the target is out of range, the parent bone is scaled to reach it. If more than one bone is being constrained and the parent bone has local nonuniform scale, stretch is not applied. Assume false if omitted.
Transform constraint timeline
The transform section of an animation describes timelines for transform constraints.
Example transform constraint animation JSON:
"constraintName": [
{ "time": 1.81, "rotateMix": 0.66, "translateMix": 0, "scaleMix": 0.5, "shearMix": 0.5 },
...
],
...
},
Transform constraint keyframe attributes:
- time: The time in seconds for the keyframe.
- rotateMix: The transform constraint rotate mix for the keyframe. Assume 1 if omitted.
- translateMix: The transform constraint translate mix for the keyframe. Assume 1 if omitted.
- scaleMix: The transform constraint scale mix for the keyframe. Assume 1 if omitted.
- shearMix: The transform constraint shear mix for the keyframe. Assume 1 if omitted.
Path constraint timelines
The path section of an animation describes timelines for path constraints.
Example path constraint animation JSON:
"constraintName":
"position": [
{ "time": 1.81, "position": 0.7 },
...
],
"spacing": [
{ "time": 2.92, "spacing": 0.05 },
...
],
"mix": [
{ "time": 3.03, "rotateMix": 0.5, "translateMix": 0.75 },
...
],
...
},
Path constraint keyframe attributes:
- time: The time in seconds for the keyframe.
- position: The position constraint position for the keyframe. Assume 1 if omitted.
- spacing: The position constraint spacing for the keyframe. Assume 1 if omitted.
- rotateMix: The position constraint rotate mix for the keyframe. Assume 1 if omitted.
- translateMix: The position constraint translate mix for the keyframe. Assume 1 if omitted.
Deform timeline
The deform section of an animation describes timelines for each mesh attachment to manipulate vertices.
Example deform animation JSON:
"skinName": {
"slotName": {
"meshName": [
{
"time": 0,
"curve": [ 0.25, 0, 0.75, 1 ]
},
{
"time": 1.5,
"offset": 12,
"vertices": [ -0.75588, -3.68987, -1.01898, -2.97404, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
-1.01898, -2.97404, -0.75588, -3.68987, 0, 0, -0.75588, -3.68987, -0.75588, -3.68987,
-1.01898, -2.97404, -1.01898, -2.97404, -1.01898, -2.97404, -0.75588, -3.68987 ],
"curve": [ 0.25, 0, 0.75, 1 ]
},
...
],
...
},
...
},
...
}
Deform keyframe attributes:
- time: The time in seconds for the keyframe.
- offset: The number of vertices to skip before applying vertices. Assume vertices <= offset are 0.
- vertices: A list of number pairs that are the amounts to add to the setup vertex positions for the keyframe. If there are fewer entries than vertices, assume vertices after these are 0.
- curve: The interpolation to use between this and the next keyframe. If the attribute is omitted the curve is linear, if the value is the string "stepped" the curve is stepped, otherwise the value is
cx1for a Bézier curve.
A Bézier curve has 4 elements which define the control points:cx1,cy1,cx2,cy2. The X axis is from 0 to 1 and represents the percent of time between the two keyframes. The Y axis is from 0 to 1 and represents the percent of the difference between the keyframe's values. - c2: The
cy1value for a Bézier curve. Assume 0 if omitted. - c3: The
cx2value for a Bézier curve. Assume 1 if omitted. - c4: The
cy2value for a Bézier curve. Assume 1 if omitted.
Event timeline
The events section of an animation describes a single timeline for triggering events.
Example events animation JSON:
{ "time": 0.2, "name": "event1", "int": 1, "float": 2, "string": "three" },
{ "time": 0.6, "name": "event2", "int": 4, "float": 5, "string": "six" },
...
}
Event keyframe attributes:
- time: The time in seconds for the keyframe.
- name: The name of the event.
- int: The integer value of the event. Assume the setup pose value if omitted.
- float: The float value of the event. Assume the setup pose value if omitted.
- string: The string value of the event. Assume the setup pose value if omitted.
- volume: The volume used to play the audio file. Assume the setup pose value if omitted.
- balance: The stereo balance used to play the audio file. Assume the setup pose value if omitted.
Draw order timeline
The draworder section of an animation describes a single timeline for changing the draw order, which is a list of slots on the skeleton in the order that their attachments should be drawn.
Example draworder animation JSON:
{
"time": 0.2,
"offsets": [
{ "slot": "slotName", "offset": 1 },
{ "slot": "slotName", "offset": -2 },
...
]
},
...
}
Draw order keyframe attributes:
- time: The time in seconds for the keyframe.
- offsets: A list of slot names and numeric offsets, which are the number of draw order entries to shift the specified slot relative to its setup pose draw order index. If "offsets" is omitted, the keyframe will set the draw order to the setup pose draw order.
